Cyprus Sees Surge in Debt-to-GDP Ratio, According to Eurostat
When Juxtaposed With the Second Quarter of 2022, Cyprus Experienced an 8.1 Percentage Point Reduction, the Third-Largest Decrease in the EU
Cyprus's gross debt-to-GDP ratio surged by 2.2 percentage points to 85.3% by the end of the second quarter of 2023, the most significant increase among EU member states when compared to the first quarter of the same year. These findings come from the latest data released by Eurostat, the European Union's statistical service. Notably, when juxtaposed with the second quarter of 2022, Cyprus experienced an 8.1 percentage point reduction, the third-largest decrease in the EU.
Meanwhile, the broader eurozone registered a slight decline in this ratio, down to 90.3% in the second quarter from 90.7% in the first. On an EU-wide level, the metric decreased to 83.1% from 83.4%.
This decline across both the eurozone and the EU is largely attributed to the absolute increase in GDP outpacing the rise in public debt.
Comparing year-over-year figures, the ratio for the eurozone fell from 93.5% in the second quarter of 2022 to 90.3% in 2023. For the EU, the drop was from 85.9% to 83.1%.

Meanwhile, the broader eurozone registered a slight decline in this ratio, down to 90.3% in the second quarter from 90.7% in the first. On an EU-wide level, the metric decreased to 83.1% from 83.4%.
This decline across both the eurozone and the EU is largely attributed to the absolute increase in GDP outpacing the rise in public debt.
Comparing year-over-year figures, the ratio for the eurozone fell from 93.5% in the second quarter of 2022 to 90.3% in 2023. For the EU, the drop was from 85.9% to 83.1%.
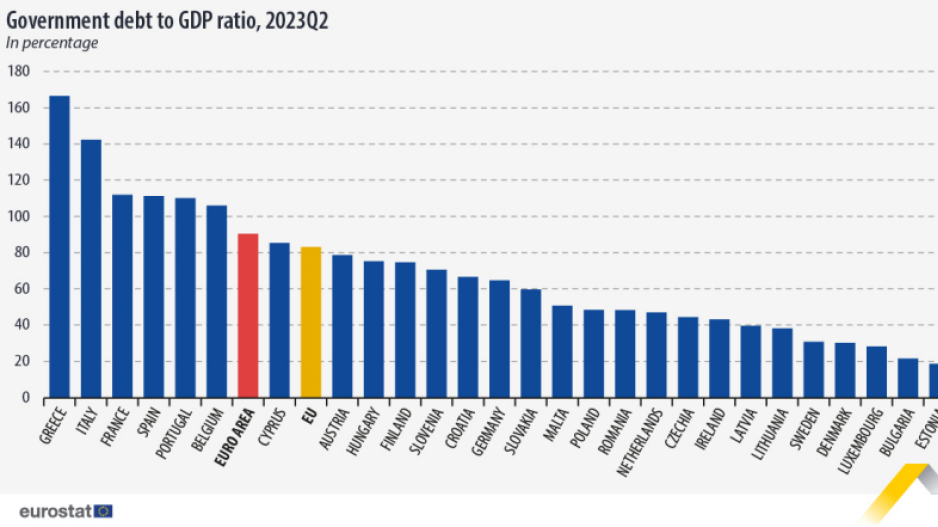
Of all member states, Greece recorded the highest public debt-to-GDP ratio in the second quarter of 2023 at 166.5%. Following were Italy (142.4%), France (111.9%), Spain (111.2%), Portugal (110.1%), and Belgium (106.0%). On the other end of the spectrum, Estonia had the lowest at 18.5%, trailed by Bulgaria (21.5%), Luxembourg (28.2%), Denmark (30.2%), and Sweden (30.7%).
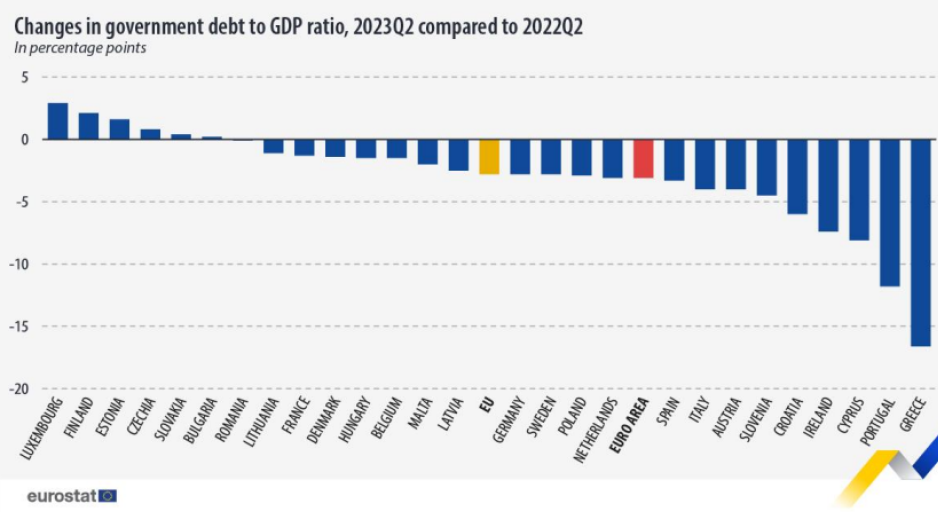
In terms of quarterly changes from the first to the second quarter of 2023, the debt-to-GDP ratio rose in nine member states and fell in 18. Cyprus saw the largest increase (+2.2 points), with significant hikes also in Slovakia, Italy, Finland, and Estonia. Conversely, the most notable decreases were observed in Latvia, Croatia, Portugal, Greece, and Malta, among others.
Comparing the second quarter of 2023 with the same period in 2022, the ratio increased in six member states and decreased in 21. Luxembourg, Finland, Estonia, and the Czech Republic are among the countries where the ratio rose, while Greece, Portugal, Cyprus, and Ireland experienced significant reductions.
By the close of the second quarter in 2023, bonds represented 83.4% of the debt in the eurozone and 82.9% in the EU. Loans accounted for 13.8% in the eurozone and 14.3% in the EU, with currency and deposits making up 2.8% and 2.7% respectively.
Due to the participation of EU member state governments in granting loans to certain member states, Eurostat also releases quarterly data on intergovernmental lending (IGL). By the end of Q2 2023, IGL as a percentage of GDP stood at 1.6% for the eurozone, 1.3% for the EU, and 1.1% for Cyprus.