ROBO - Cyprus-based Robot Makers and Why They Matter
"It is definitely more challenging doing so on an island, but it is more than doable and profitable. No excuses. Go for it!"
Having a handy robot companion like R2D2 from Star Wars is by no means remotely close to being produced or commercially available. Achieving such a milestone feels far-fetched, and something that still belongs in sci-fi films. However, robot makers globally are taking steps towards enabling people to carry-out their professions and tasks in a more risk averse environment through automating certain processes and duties. They are even being incorporated in schools, and are assumed to be able to support declining workforces.
The robotics industry has vastly evolved since 1960 when General Motors (GM) purchased the first industrial robot, geared to assist in stacking pieces of hot metal. It cost GM $18,000 (today’s equivalent of $180,000). Today, robots are integrated with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) and help businesses across various industries perform mundane, difficult, and dangerous tasks, making room for creativity and communication between humans.
Just as many evolving technologies, the global robotics market holds tremendous value. The total market value in robotics worldwide in 2022 was at $34 billion, and is projected to grow to $45 billion by 2028.
Several notable organizations like Universal Robots, Aldebaran, and iRobot showcase the versatile application of robots in the industrial, educational, and consumer robot maker landscape. A core, leading stakeholder in the industry, the International Federation of Robotics, is a non-profit organization established in 1987 which brings stakeholders together to promote robotics.
It is vital to recognize, however, the local endeavors that are making a mark around the world. Among these local endeavors is Cyprus-based innovative robot maker, ROBO, which focuses on enabling and empowering robot makers in Cyprus and the European Union by designing, producing, and distributing robotics and software tools locally and regionally.
The most common application of robotics today are industrial robots, assisting in welding, material and machine handling, assembly, painting, and more. There are also growing markets for humanoid robots and household robots, with projected compound annual growth rates of 52.8 percent and 18.81 percent respectively.
The World Economic Forum highlights a study on the impact of robotic technology adoption on employment within organizations, where co-author Lynn Wu expressed that, “any employment loss in our data we found came from the non-adopting firms. These firms became less productive, relative to the adopters. They lost their competitive advantage and, as a result, they had to lay off workers.”
The study suggests that, contrary to popular belief, instead of robots replacing humans in the workplace, they will actually enable them to lead more creative and challenging tasks by automating the more mundane and repetitive tasks.
Wu’s statement accentuates the necessity of adjusting to the future of automating work. In doing so, organizations enable staff to focus on more creative tasks that require critical thinking and collaboration. Research indicates that workplaces are expected to experience a 30% rise in productivity when adopting robotics. Robotic companies are constantly on the look-out for ways to improve their robots in ways that serve the specific needs of industries to optimize their impact.
Universal Robots (UR) has made significant contributions to industries through their collaborative robot (cobots) technology. By developing robots that can work alongside humans safely, Universal Robots has revolutionized manufacturing processes. For example, UR worked with Siemens Geratewerk Erlangen (GWE), a large plant driving digitalization for Siemens, dedicated to implementing production efficiencies. The plant uses 70 UR cobots to take mundane tasks off of employees hands through automation.
Moving away from robotic arms and production efficiencies, Aldebaran, formerly SoftBank Robotics Group, has been leading the humanoid robot market since 2005. Aldebaran was acquired by the United Robotics Group (URG) in 2022, setting URG among the leading service robotics companies across Europe. Their humanoid robots have been implemented in schools, helping children learn to build social skills and self-confidence.
Less humanoid, but still ‘domesticated’ robots which are more commonly known are iRobot’s Roombas, automating vacuuming and mopping in households. iRobot, founded in 1990 by Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), the company’s household robot sales today exceed 40 million units globally. Despite being widely known for their now staple product, the Roomba, created in 2002, iRobot has contributed to unraveling mysteries shrouding the Great Pyramid of Giza, and saving lives across conflict zones.
Their mobile robot has been zooming across household floors for nearly two decades. It uses a “bump and turn” method of navigation, leading people to take to social media, displaying humourous and innovative modifications made to their Roomba’s, such as programming it to yell out loud when it collides with an object. This navigation method, however, had sparked controversy due to iRobot’s vision to use that data to map out the future of smart homes.
The future of robot making is heavily aligned with AI integration. Dwight Klappich, Vice President and Fellow in Gartner’s Supply Chain Practice, expressed in Gartner’s Hype Cycle for Mobile Robots and Drones, 2023, that “labor shortages and challenges retaining talent, coupled with technology advances such as machine learning and AI, will continue to drive adoption of smart robots.”
As companies look to continuously optimize their operations through automation, the development of robots brought to life through AI will shape the future of work.
Innovation in robotics, however, would not be possible without organizations and industry leaders providing platforms and innovative methods to enable people to learn how to build, design, and program robots. Enter one of Cyprus’ leading robot makers - ROBO.
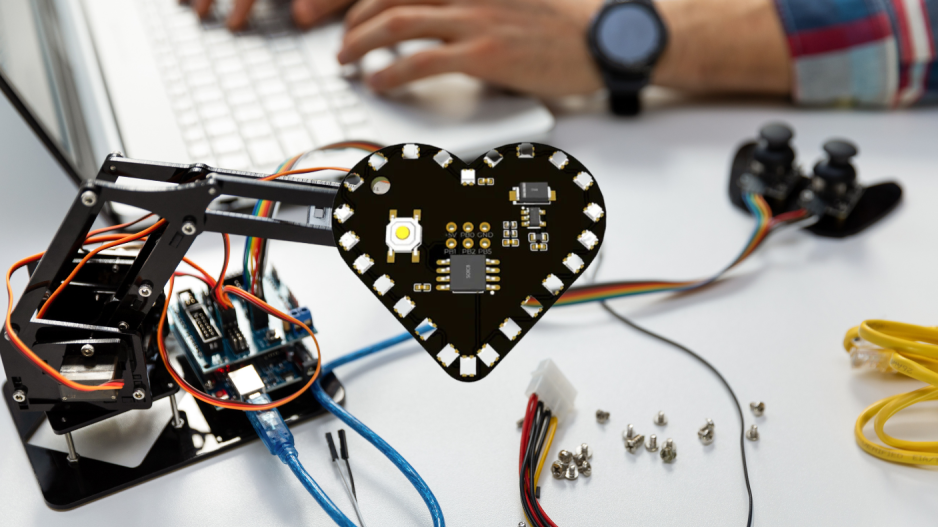
The impact of the Cypriot robot maker community goes beyond local boundaries. As businesses worldwide plan for the integration of robots into their operations, the knowledge and experience gained within Cyprus become increasingly valuable. By actively participating in this global conversation, Cyprus-based robot makers ensure that their expertise and insights are shaping the future of industries within the island, and regionally.
An integral part of any industry, particularly robot making, is the access to resources pertinent to the robot industry. This is where Robo comes in to provide greater and easier access to the microcontroller, maker, and robotics world in Cyprus.
Robo is an ed-tech hardware company that focuses on creating high-quality, science-based educational material. The hardware and the supporting educational material are designed in-house to provide complete STEM-based education packages to academic centers and institutions.
By focusing on designing platforms and kits for rapid prototyping, Robo empowers Cypriots to participate in the exciting world of robotics. Their efforts have not only fueled local engagement but also garnered attention internationally, paving the way forward for Cyprus to be recognized as a hub for innovative robot makers.
Their bespoke designs for platforms and kits include an Arduino-based tank robot named Tankbot, a fun and innovative mini arcade, Tinycade, a modular pixel wall, Infinite Wall which is currently under development, and Heartbit, a small reprogrammable heart that has gone viral on TiktTok, garnering more than 300,000 interactions in a single day.
Moreover, Robo is currently heading their first international campaign. The startup is on track to launch its first crowdfunding campaign with Crowdsupply, the leading crowdfunding platform for hardware-centric initiatives. The campaign is signed and is focused on developing and manufacturing the Robo UNO+ by the end of Q4 2023.
The benefits extend to the educational landscape of Cyprus. By fostering a culture of innovation and robotics, the Cypriot robot maker is equipping the next generation with the skills needed for the future workforce.
Robo’s Managing Director, Odysseas Economides offered insights into Cyprus’ current robotics landscape, highlighting that there has been a “small uptick in professional robot making, and a bigger uptick in educational robotic learning.” He stated that Robo’s robots play a significant role, “in that they are used in schools and educational centers as a STEM tool to advance their knowledge of programming, electronings, and robotics.”
When asked about the most prevalent barriers and developments in the robot-making industry in Cyprus, Odysseas expressed that “one of the biggest hassles that a production company has in Cyprus is the sourcing and exporting of raw materials and hardware. It takes more time and money going through a production cycle on an island.”
He continued, adding that “there has been a beginning in the usage of industrial robots, like industrial robotic arms. For starters, I consider the implementation of already existing robots a much smarter route to take in Cyprus, rather than producing new ones. Very capable and advanced technology already exists. We need to put it into action in our local industry. To do so, a capable company like HardwareX is needed to be able to program (and use AI if needed) already existing industrial robots to solve industry project-specific challenges.”
For entrepreneurs and professionals seeking to explore the robot-making industry, Odysseas believes that “it is definitely more challenging doing so on an island, but it is more than doable and profitable. No excuses. Go for it!”
It is definitely more challenging doing so on an island, but it is more than doable and profitable. No excuses. Go for it!
Through initiatives like Robo, Cyprus is making significant contributions to the world of robot making, empowering individuals and businesses to remain relevant in the evolving economies of tomorrow. The future of work, especially in the industrial sector, is looking to implement AI-guided robots to collaborate with humans.
Considering the rapid pace of technological evolution and its impact on the labor landscape, it is critical for organizations such as ROBO to receive support for its efforts in education, development, and distribution of robotic components and materials. Supporting such organizations is a boon for Cyprus, in order to foster a culture of innovation and learning in a space that will likely shape the future of not only work, but life as we know it.